Healthcare Providers
Patient Guiding Handbook for Healthcare Professionals
Spot early signals of common and aggressive cancers using
next-generation of ctDNA technology
Brochure:
Healthcare Professional Handbook 18.90 MB 862 downloads
Spot early signals of common and aggressive cancers using next-generation of ctDNA...Find out:
Why is cancer screening important?
Early detection is the key to save lives.
We fear cancer. We fear the risks we think we can’t control
But we can control, and we should not fear
The answer is in the matter of time. Cancer doesn’t wait. The sooner cancer is detected, the better treatment outcomes will be.
- (1) Sankaranarayanan, R., Ramadas, K., Qiao, Y., 2014. Managing the changing burden of cancer in Asia. BMC Med 12, 3
- (2) Statistics adapted from the American Cancer Society’s (ACS) publication, Cancer Facts & Figures 2022 and Cancer Facts & Figures 2021; the ACS website; and the International Agency for Cancer Research website. (All sources accessed January 2022.)
- (3) UN & WHO: Early cancer diagnosis, better trained medics can save lives, money
How to improve our chances of early detection?
How does
SPOT-MAS test work?
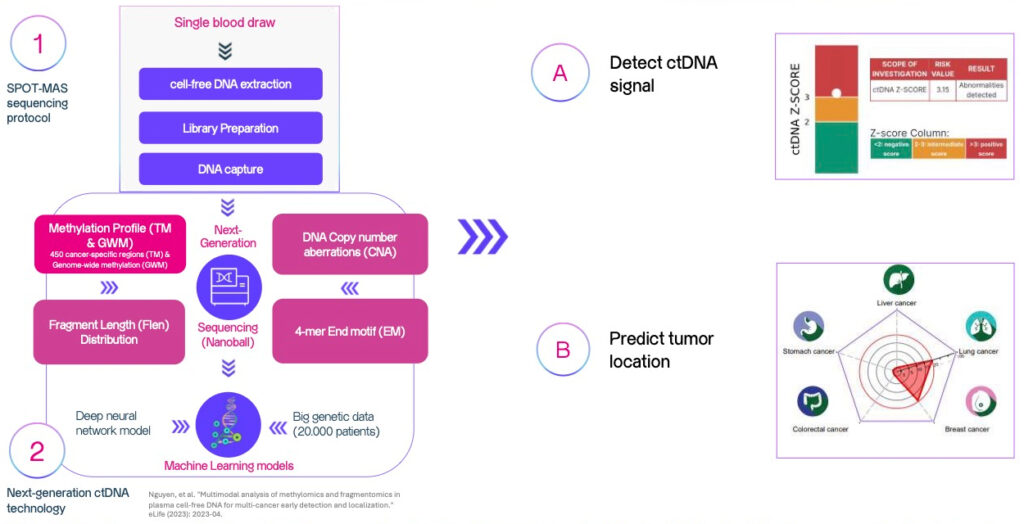
SPOT-MAS test is based on a scientific discovery of DNA fragments from tumor cells that are released into the bloodstream.
These DNA fragments are called circulating tumor DNA,
or ctDNA.
Find out:
Scope of testing (1)
Basic Option: Top 05 Common Cancers
Extended option: 05 Less Common But Aggressive Cancers
currently have no standard-of-care screening program available.(2)
These cancers accounted for 56.2% of total new incidences and 59.9% of total mortality in South-East Asia.(3)
- (1) The number of cancer types varies based on availability in different countries.
- (2) according to WHO, American Cancer Society 2024 and USPSTF recommendations.
- (3) GLOBOCAN WHO – SEA report 2022
SPOT-MAS test clinical validated performance
Case-control study
Clinical validation study
- (1) Nguyen, et al. “Multimodal analysis of methylomics and fragmentomics in plasma cell-free DNA for multi-cancer early detection and localization.” eLife (2023): 2023-04. https://elifesciences.org/articles/89083
- (2) Nguyen, et al. “Analytical and clinical validation of a ctDNA based assay for multi-cancer early detection” (2023). https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.12.22.23300420
Who is
SPOT-MAS for?
MCED tests are often prohibitively expensive, but if appropriately priced for low- and middle-income countries, assays such as SPOT-MAS have the real potential to enable early detection, particularly where national cancer screening programs are not available.
ESMO daily: Transitioning liquid biopsies from research to practice in lung cancer. (ESMO: European Society of Medical Oncology)
SPOT-MAS are NOT for people who:
- Have been diagnosed with cancer within 5 years
- Have suspected signs and symptoms of cancer (unexplained weight loss, pain does not help with medication, bleeding or abnormal discharge in the nipple, prolonged cough, disorders of bowel movements)
- Are pregnant
- Have a history of bone marrow transplant or whole blood transfusion within 3 months
Knowing the Limitations
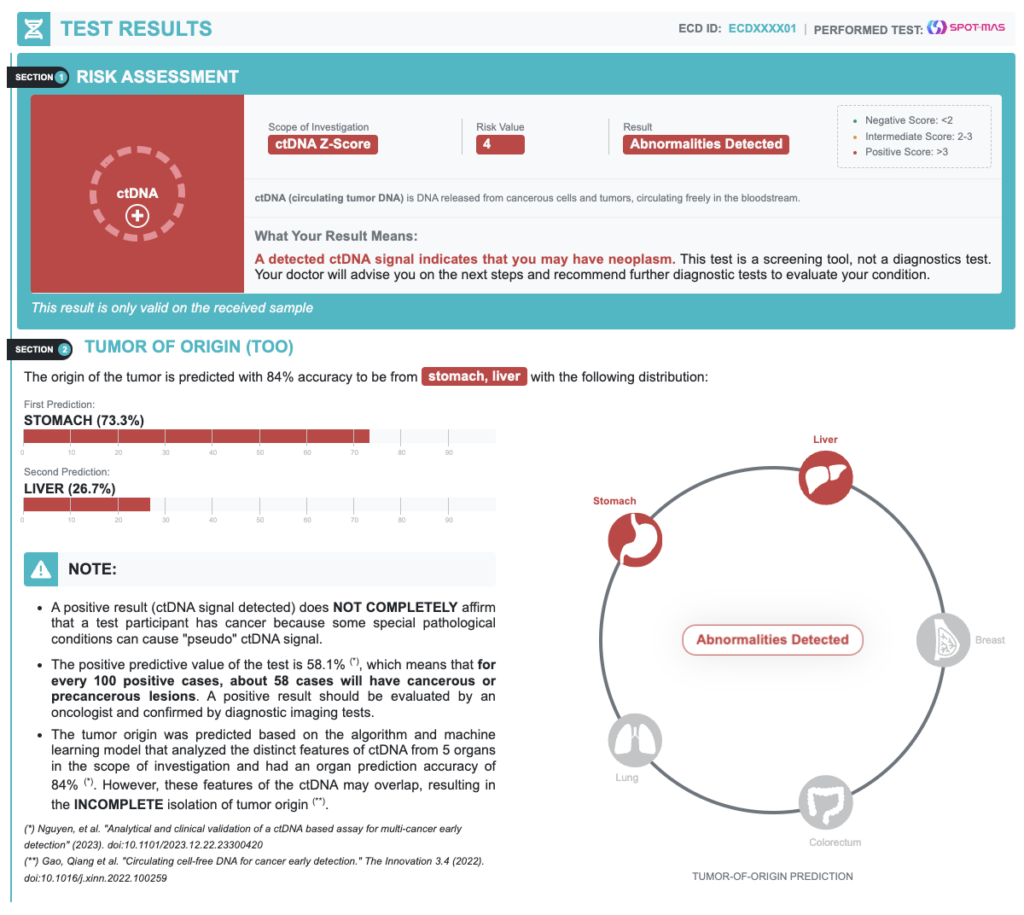
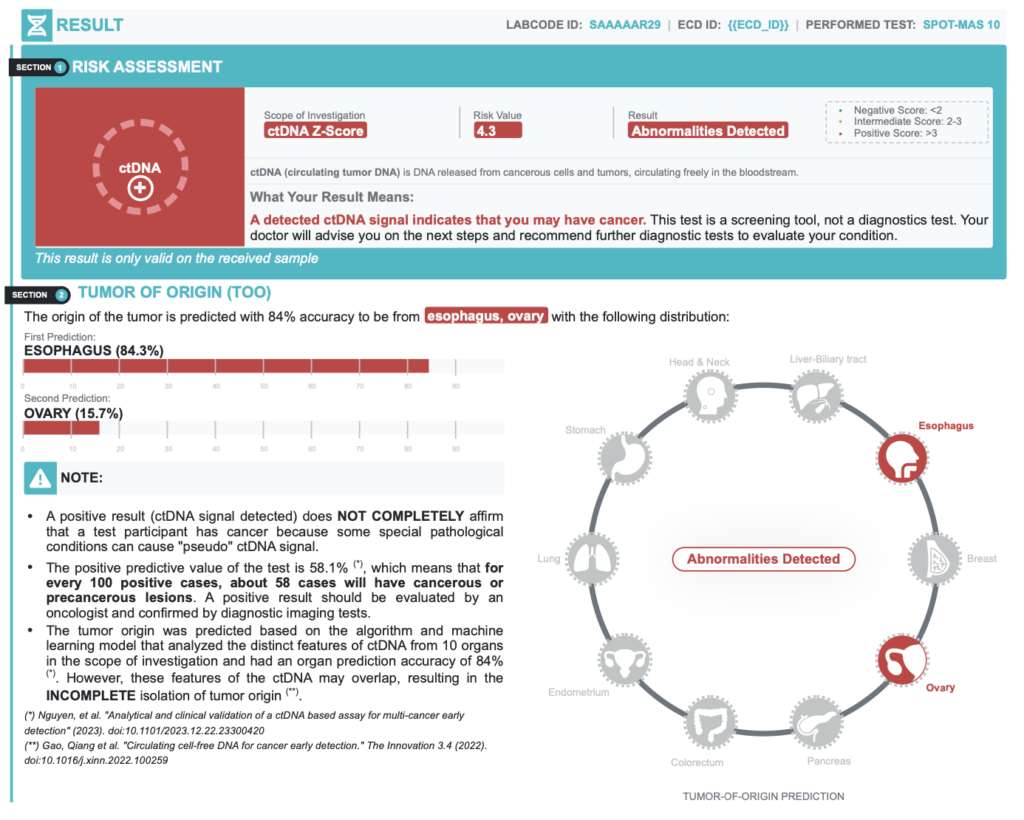
A positive result (ctDNA signal detected) does NOT COMPLETELY confirm that a test participant has cancer because some special pathological conditions can cause “pseudo” ctDNA signal.
A negative result (no ctDNA signal detected) does NOT COMPLETELY rule out the presence of cancer because
- The tumor is out of screening scope.
- Rare tumors located in an anatomic location rarely sheds ctDNA
- Rare advanced metastatic cancers with methylation changes are completely different from the primary cancer
Key Recommendations
| TEST PERFORMANCE | % | INTERPRETATION |
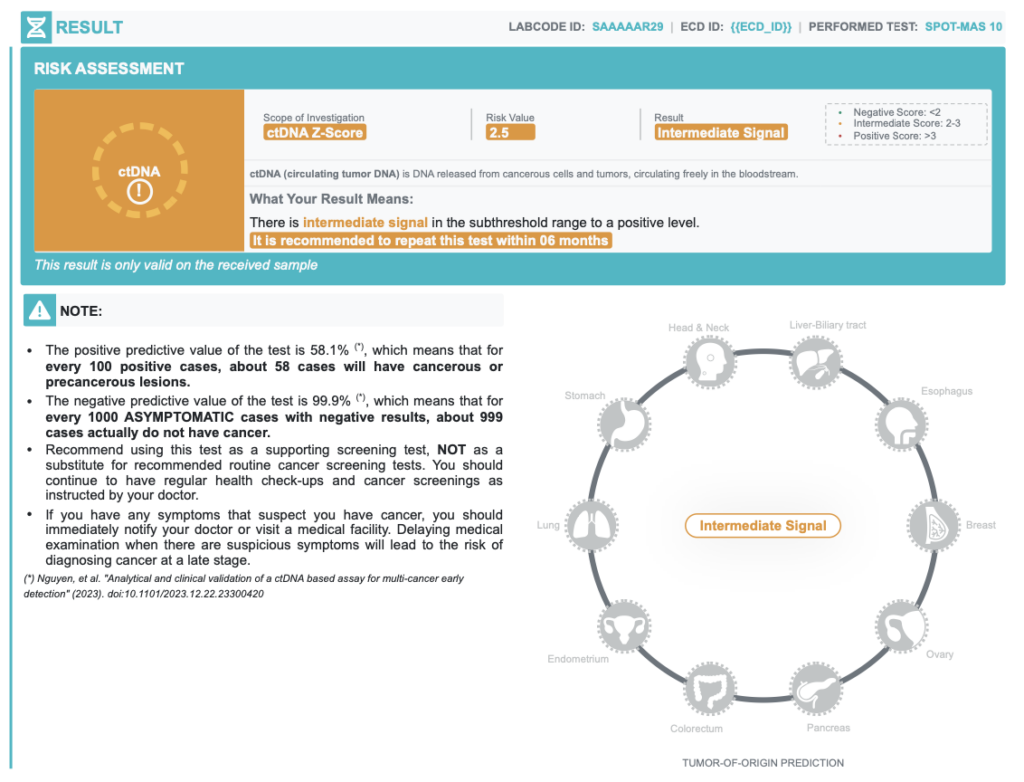
| Positive Predictive Value | 58.1% | In every 100 positive cases, about 58 cases actually have cancer |
| Negative Predictive Value | 99.9% | In every 100 negative cases, about 99 cases actually do not have cancer |
| Accuracy of Tumor Origin Prediction | 84.0% | Probability of primary tumor location prediction based on bioinformatics models |
Key recommendations:
- The SPOT-MAS test does not detect all cancers.
- False positive and false negative results can occur.
- A positive result requires confirmatory diagnostic evaluation by medically established procedures (e.g. imaging and/or tissue biopsy) to confirm cancer.
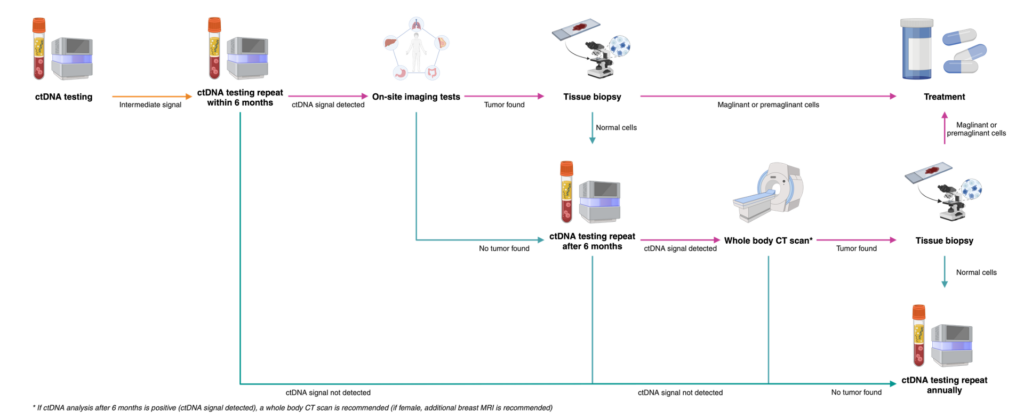
What to do with the results?
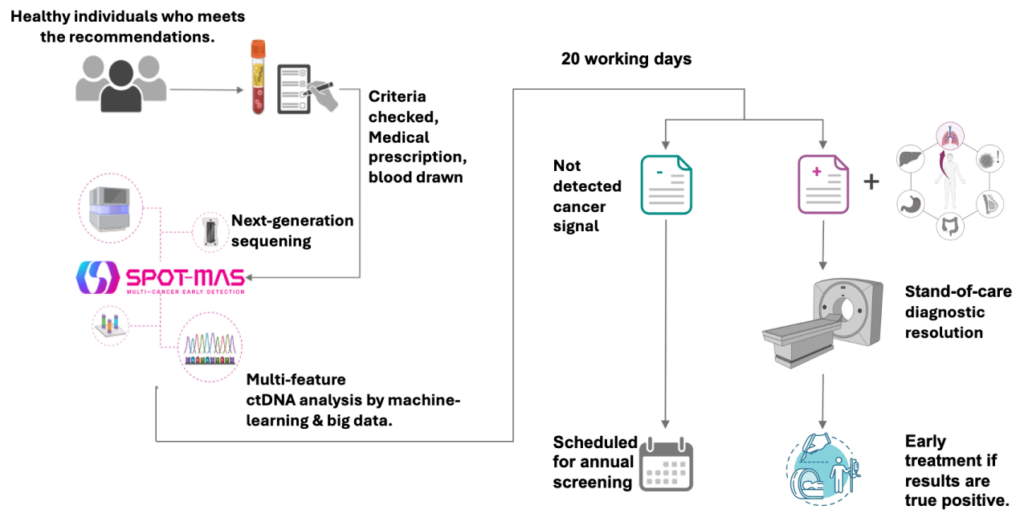
03 possible results after ctDNA analysis
Negative Result consultation
- This test does not measure the risk of developing cancer in the future.
- With a negative result, you should continue to take regular health checkups and cancer screenings as recommended according to your age and your doctor’s instructions and repeat this test annually.
INTERMEDIATE result
2 < ctDNA Zscore < 3-
Intermediate signals
Negative Result consultation
- This test does not measure the risk of developing cancer in the future.
- With a negative result, you should continue to take regular health checkups and cancer screenings as recommended according to your age and your doctor’s instructions and repeat this test annually.
Positive Result – Recommended diagnostic resolution
| TUMOR ORIGIN PREDICTION | RECOMMENDED DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING TESTS |
| Breast | Breast ultrasound combine with mammography OR breast MRI (if mammogram was taken within 3 months) |
| Liver-biliary tract | Triple phase abdominal CT scan |
| Lung | Chest CT scan with contrast |
| Colorectum | Colonoscopy |
| Stomach | Upper endoscopy |
| 05 extended cancers: Esophagus, Pancreas, Ovary, Uterine, Biliary tract | Chest and abdominal CT scan with contrast (if customer is female, add transvaginal ultrasound) |
| Other organs | Whole body CT scan (if customer is female, add breast MRI) |